Urban Design: MasterPlanGAN

Helpful Links:
Ye, X., Du, J., & Ye, Y. (2022). MasterplanGAN: Facilitating the smart rendering of urban master plans via generative adversarial networks. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 49(3), 794-814. https://doi.org/10.1177/23998083211023516
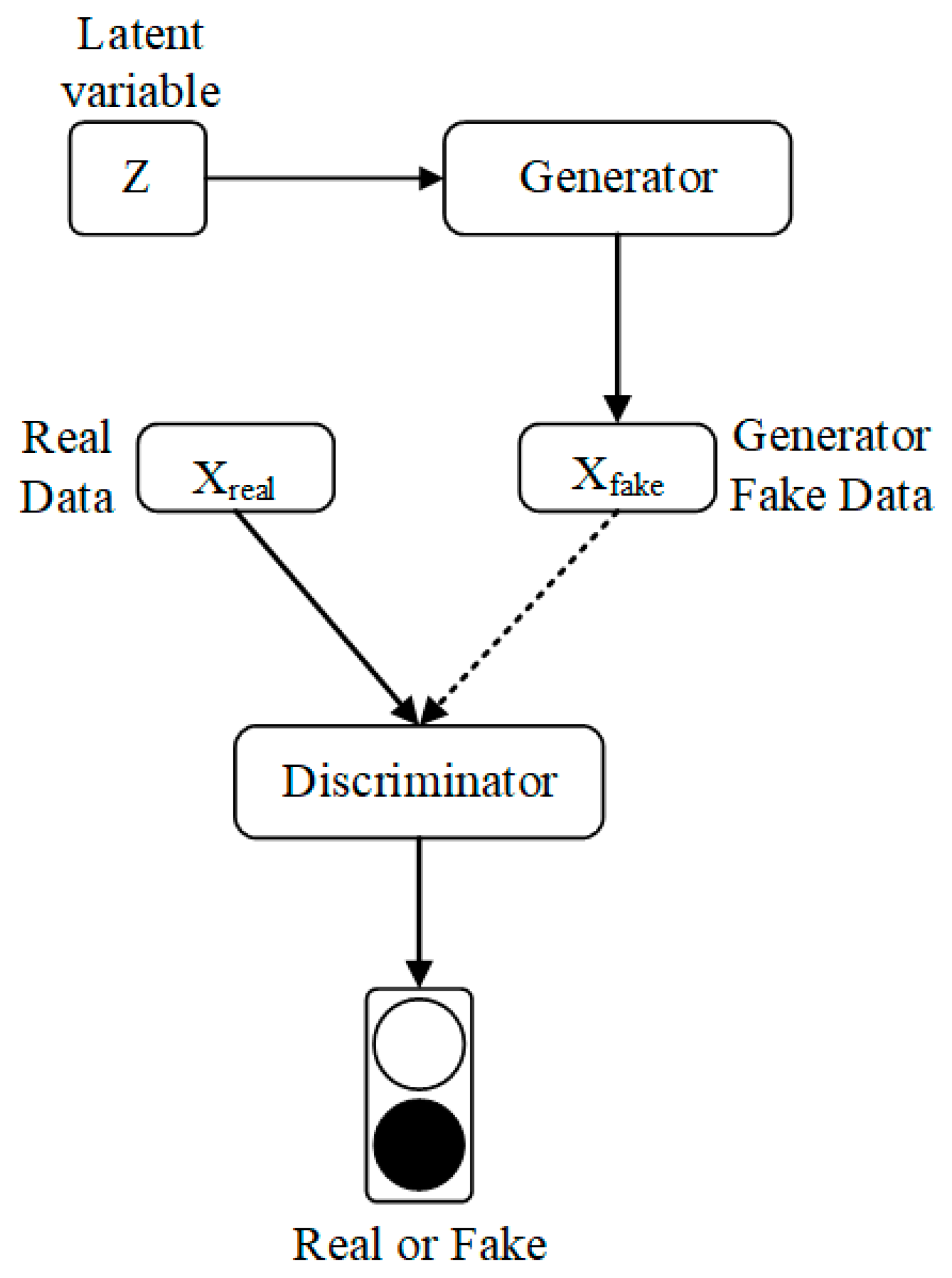
This study proposes a prototype for the smart rendering of urban master plans via artificial intelligence algorithms, a process which is time-consuming and relies on professional experience. With the help of crowdsourced data and generative adversarial networks (GAN), a generation model was trained to provide colorful rendering of master plans similar to those produced by experienced urban designers.
Approximately 5000 master plans from Pinterest were processed and CycleGAN was applied as the core algorithm to build this model, the so-called MasterplanGAN. Using the uncolored input design files in an AutoCAD format, the MasterplanGAN can provide master plan renderings within a few seconds. The validation of the generated results was achieved using quantitative and qualitative judgments.
The achievements of this study contribute to the development of automatic generation of previously subjective and experience-oriented processes, which can serve as a useful tool for urban designers and planners to save time in real projects. It also contributes to push the methodological boundaries of urban design by addressing urban design requirements with new urban data and new techniques. This initial exploration indicates that a large but clear picture of computational urban design can be presented, integrating scientific thinking, design, and computer techniques.
Simulating Urban Growth
Traffic and Mobility Modelling
Generative Design of Infrastructure

Helpful Links:
- Generative design in civil construction: a case study in Brazil
- Generative AI-enabled Vehicular Networks: Fundamentals, Framework, and Case Study
- Infrastructure for a RAG-capable generative AI application using Vertex AI
- Exploring Generative Design in Critical Infrastructure
- 15 Generative AI Enterprise Use Cases
- Generative urban design: A systematic review on problem formulation, design generation, and decision-making
- Generative urban design: A systematic review on problem formulation, design generation, and decision-making
The application of generative design in infrastructure development has shown promising results across various projects and studies. For instance, a case study involving Autodesk’s tools—Civil 3D for optimization and Dynamo for computational design—illustrated the benefits of generative design in the layout and construction of a rail maintenance facility, addressing complex design challenges effectively.
Similarly, a study from Brazil delved into the integration of generative design in civil construction, utilizing advanced AI techniques such as genetic algorithms, graph-based machine learning, and generative adversarial networks. These technologies were combined with Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Algorithmic-Aided Design (AAD) to produce innovative, efficient, and sustainable architectural and urban planning solutions. These examples underscore the transformative impact of generative AI in enhancing the design, optimization, and implementation of critical infrastructure, paving the way for more efficient and resilient urban and industrial environments. From streamlining equipment layouts in power plants and water treatment facilities to improving urban planning and transportation systems, generative design fosters more efficient, adaptable, and resilient infrastructures, which are imperative for meeting future challenges and community needs.
Generative design, combined with AI, is being used to optimize the design of critical infrastructure like power plants, water treatment facilities, and transportation systems. Generative algorithms can be utilized to streamline the complex task of arranging equipment and spaces within these facilities, ensuring optimal layout and coordination. The Asian Development Bank (ADB) and Dhaka Water Supply and Sewerage Authority (Dhaka WASA) used the Transcend Design Generator’s generative design capabilities to optimize the layout and operation of a water treatment facility., leading to significant reductions in project risk and compressed the planning phase from 8-10 months to just 8-12 weeks. Generative design facilitated by AI can create infrastructure that is not only efficient but also adaptable and resilient to future changes.
Generative design can help reduce waste and resource consumption by preemptively considering future adaptability and expansion needs in the initial design phase. Generative design can improve space utilization and enhance the flow of transportation systems, reducing congestion and environmental impact.
Environmental and Climate Predictions
Generative AI techniques, such as deep learning and neural networks, are enhancing the precision and efficiency of climate models by improving the representation of complex weather phenomena like precipitation patterns, as illustrated in studies using physically constrained generative adversarial networks.
Concurrently, these techniques are revolutionizing weather forecasting by enabling meteorologists to process vast datasets in real time, significantly enhancing both short-term and long-term predictions. This progress is vital for climate change adaptation and disaster management, potentially reducing the impact on vulnerable populations.
Additionally, generative AI tools are being leveraged to boost climate literacy among the general public, with tools like ChatGPT providing accurate responses to climate-related queries, thereby aligning well with established hazard risk indices.
Moreover, climate tech startups are adopting generative AI for tasks ranging from generating synthetic data for predictive modeling to increasing manufacturing efficiencies while emphasizing the need for sustainable AI practices.
Collectively, these advancements underscore the transformative role of generative AI in climate science, promising further innovations in tackling the multifaceted challenges of climate change.
Public Space Design and Utilization

Helpful Links:
- Image Generative AI to Design Public Spaces: a Reflection of how AI Could Improve Co-Design of Public Parks
- Generation AI: Reimagining public spaces with Victor Au-Yeung
- The Potential of Generative AI to Help Cities Better Manage Their Public Parks and Green Spaces
- Designing for the Public Sector with Generative AI
- Generative Urban AI Is Here. Are Cities Ready?
- AI Tools to Synthesize Characteristics of Public Spaces
- The best publicly available use cases for generative AI
Generative AI is increasingly pivotal in the design and management of public spaces, enhancing both the creative processes and practical aspects. A study highlighted in the ACM journal utilized image generative AI (IGAI) tools like Dream Studio AI to foster community involvement in the design of the Puente Hills Landfill Park in Los Angeles. By generating visual interpretations from immigrant interviewees’ insights, the project facilitated a deeper engagement with community members, critically reflected through subsequent workshops and interviews.
Concurrently, an Adobe blog post showcased how architect Victor Au-Yeung applied generative AI tools, such as Generative Fill in Adobe Photoshop, to reimagine Sydney Town Hall into a more democratic space with accessible forums and galleries.In New Jersey, text-guided image-to-image translation techniques were utilized generate a collective vision for a future public space in Jersey City, which can be used as feedback and a starting point for the design process. This shift allows designers to transcend traditional constraints, quickly iterating on visionary concepts. Additionally, a post on Maket.ai discussed the use of generative AI in optimizing public park management. By analyzing data on park usage and weather conditions, AI can propose personalized maintenance schedules and identify optimal locations for new amenities, enhancing accessibility and user experience. Together, these case studies demonstrate how generative AI can revolutionize the design, iteration, and maintenance of public spaces, making them more adaptable to community needs and environmental conditions.
Generative AI is freeing creators to think beyond the rules and regulations of industries like architecture, allowing them to quickly envision and iterate on design concepts. AI can analyze park usage data and weather patterns to create personalized maintenance schedules, as well as identify the best locations for new parks and accessibility features.